To prevent system cross-contamination, the FDA "Guide to Inspections of High Purity Water Systems" recommends WFI heat exchangers employ a double-tube-plate design or continuously monitor the pressure differential on both sides, ensuring that the clean side pressure is higher than the non-clean side. ASME BPE "Bioprocessing Equipment" offers related requirements on the design, manufacturing, and inspection of double-tube-plate heat exchangers. Additionally, because the heat exchange tubes of double-tube-plate heat exchangers are easy to clean, which helps inhibit microbial growth, double-tube-plate WFI heat exchangers are widely used in the biopharmaceutical industry.
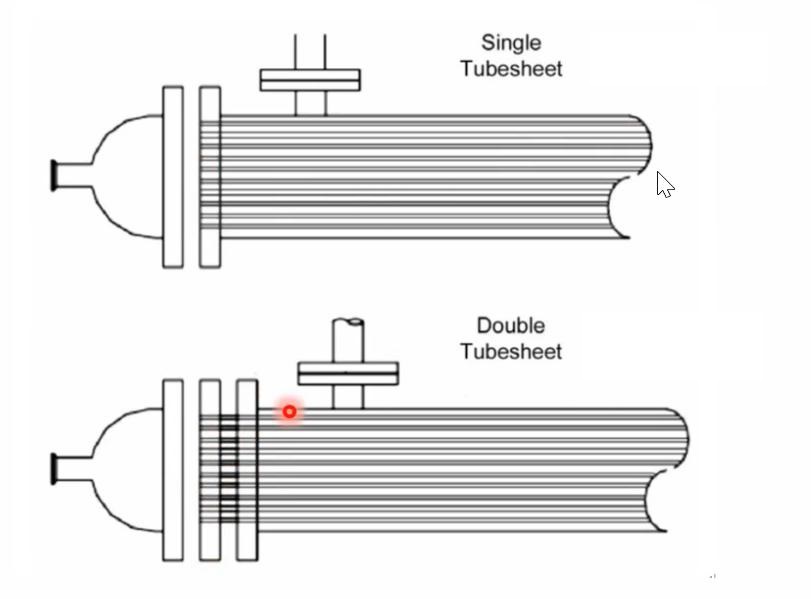
A double-tube heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat from a hot fluid to a cold fluid. It mainly consists of a shell, inner and outer tube sheets, heat exchange tubes, end caps, and baffle plates. During heat exchange, one fluid enters through a nozzle on the end cap, flows through the heat exchange tubes, transfers heat, and exits through a nozzle on the other end cap. The other fluid enters through a nozzle on the shell, flows inside the shell, transfers heat by contacting the outer walls of the heat exchange tubes, and finally exits through another nozzle on the shell.
Pre-treat raw water to meet the requirements for reverse osmosis feed water.Due to the system's design considerations and heat exchange costs, double-tube-plate heat exchangers are generally not used; plate heat exchangers are typically used under normal circumstances.
Continuously and steadily "purify" raw water into pharmaceutical water that meets pharmacopeia requirements, PW preparation usually uses plate heat exchangers (special circumstances may consider using double-tube-plate heat exchangers), and in the preparation of WFI, WFI heat exchangers are modularly provided with the entire preparation unit, such as in a distillation machine.
The storage and distribution unit includes storage units, distribution units, and point-of-use pipe network units. The distribution system is the core unit of the entire storage and distribution system and uses double-tube-plate WFI heat exchangers most frequently. It primarily serves to deliver pharmaceutical water to required process stations with certain buffering power, meeting their flow, pressure, and temperature requirements while maintaining the water quality to meet standards.
Operating condition: Circulation condition
General process conditions: 80℃→120℃, 1~2bar (g) / 3bar (g) ± steam heating
Medium: Injectable water / Industrial steam
Operating condition: Circulation condition
General process conditions: 70~80℃, atmospheric pressure / usually 3bar (g) Industrial steam heating
Medium: Injectable water / Industrial steam
Operating condition: Instantaneous condition (for equipment cleaning points, ingredient points, etc.)
Process conditions: Various process conditions, according to actual process requirements
Medium: Injectable water / Utilities
The above WFI heat exchanger operating conditions are distinguished by temperature status. For instance, heat exchangers with stable temperature conditions have a heat flow magnitude that does not vary with time within a specified area. This situation generally occurs in point-of-use pipe network units, such as the aforementioned instantaneous conditions. On the other hand, heat exchangers with unstable temperature conditions have heat flow or temperature on the heat transfer surface that changes over time, such as in mixing vessels like preparation tanks, CIP cleaning tanks, etc. When a large heat exchange area is required, heat exchangers are set outside the container, and external circulation heating or cooling is employed via a pump, as mentioned above in circulation conditions.


